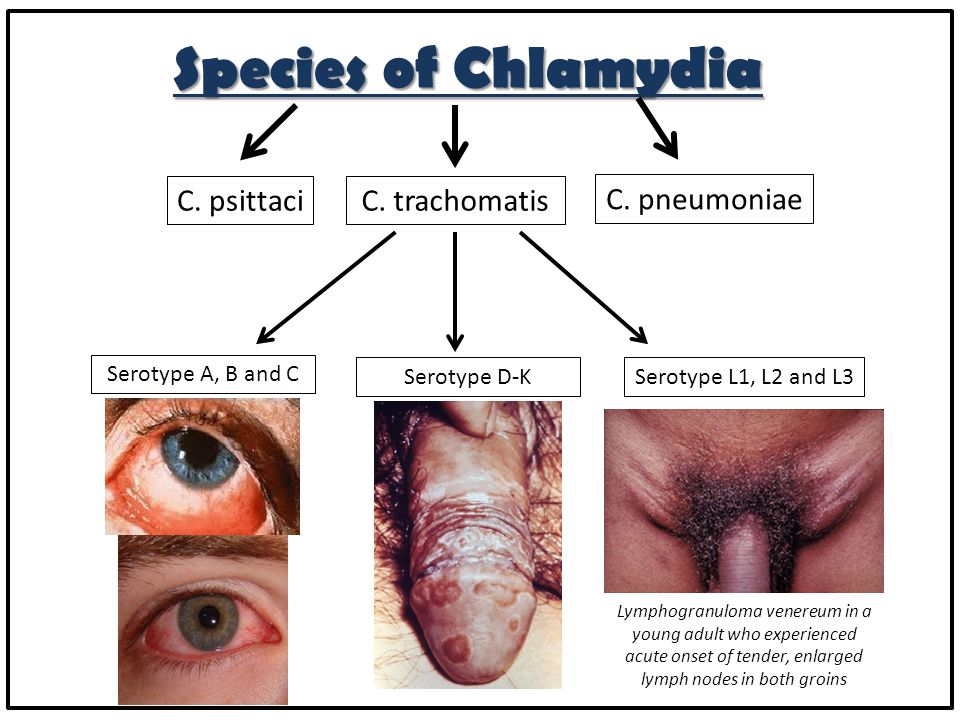
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is the most commonly reported STD in the U.S. It's spread mostly by vaginal or anal sex, but you can get it through oral sex, too. Sometimes you'll notice an odd discharge from your vagina or penis, or pain or burning when you pee. But only about 25% of women and 50% of men get symptoms.
Chlamydia is caused by bacteria, so it's treated with antibiotics. After you are treated, you should get retested in three months, even if your partner has been treated as well.
Chlamydia (kluh-MID-e-uh) trachomatis (truh-KOH-muh-tis) is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by bacteria. You may not know you have chlamydia because many people never develop the signs or symptoms, such as genital pain and discharge from the vagina or penis.
Chlamydia trachomatis affects both men and women and occurs in all age groups, though it's most prevalent among young women. Chlamydia isn't difficult to treat once you know you have it. If left untreated, however, it can lead to more-serious health problems.
Symptoms
Early-stage Chlamydia trachomatis infections often cause few or no signs and symptoms. When signs or symptoms occur, they usually start one to two weeks after exposure to chlamydia. Even when signs and symptoms occur, they're often mild and passing, making them easy to overlook.Signs and symptoms of chlamydia trachomatis infection may include:
- Painful urination
- Lower abdominal pain
- Vaginal discharge in women
- Discharge from the penis in men
- Painful sexual intercourse in women
- Bleeding between periods and after sex in women
- Testicular pain in men
It's also possible to acquire chlamydial eye infections (conjunctivitis) through contact with infected secretions.
When to see a doctor
See your doctor if you have a discharge from your vagina, penis or rectum, or if you have pain during urination. Also, see your doctor if your sexual partner reveals that he or she has chlamydia. Your doctor will likely prescribe an antibiotic even if you have no symptoms.Causes
Chlamydia trachomatis is caused by
Chlamydia trachomatis bacterium and is most commonly spread through
vaginal, oral and anal sex. It's also possible for a mother to spread
chlamydia to her child during delivery, causing pneumonia or a serious
eye infection in her newborn.
Risk factors
Factors that increase your risk of chlamydia trachomatis include:- Being sexually active before age 25
- Multiple sex partners within the past year
- Not using a condom consistent
- Other sexually transmitted infections. People who have chlamydia trachomatis are at higher risk of also having other STIs — including gonorrhea and HIV, the virus that causes AIDS.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). PID is an infection of the uterus and fallopian tubes that causes pelvic pain and fever. Severe infections may require hospitalization for intravenous antibiotics. PID can damage the fallopian tubes, ovaries and uterus, including the cervix.
- Infection near the testicles (epididymitis). A chlamydia infection can inflame the coiled tube located beside each testicle (epididymis). The infection may result in fever, scrotal pain and swelling.
- Prostate gland infection. The chlamydia organism can spread to a man's prostate gland. Prostatitis may result in pain during or after sex, fever and chills, painful urination, and lower back pain.
- Infections in newborns. The chlamydia infection can pass from the vaginal canal to your child during delivery, causing pneumonia or a serious eye infection.
- Infertility. Chlamydia infections — even those that produce no signs or symptoms — can cause scarring and obstruction in the fallopian tubes, which may make women infertile.
- Reactive arthritis. People who have chlamydia
trachomatis are at higher risk of developing reactive arthritis, also
known as Reiter's syndrome. This condition typically affects the joints,
eyes and urethra — the tube that carries urine from your bladder to
outside of your body.
Diagnosis
- A urine test. A sample of your urine analyzed in the laboratory may indicate the presence of this infection.
-
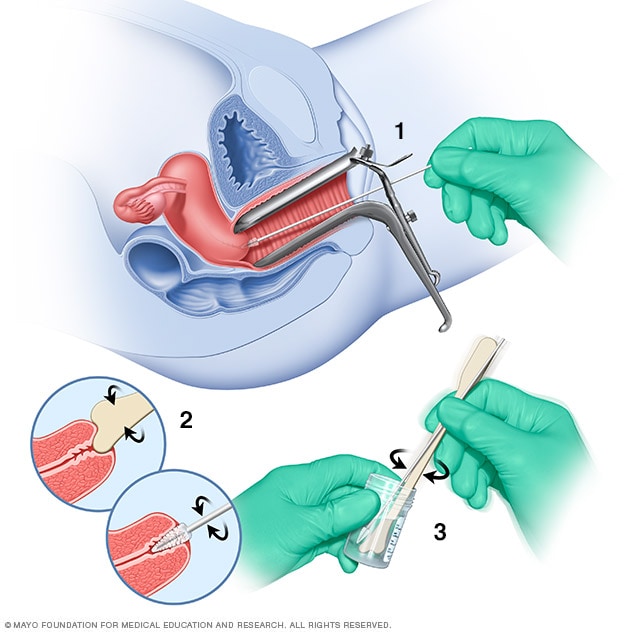
A swab. For women, your doctor takes a swab of
the discharge from your cervix for culture or antigen testing for
chlamydia. This can be done during a routine Pap test. Some women prefer
to swab their vaginas themselves, which has been shown to be as
diagnostic as doctor-obtained swabs.
For men, your doctor inserts a slim swab into the end of your penis to get a sample from the urethra. In some cases, your doctor may swab the anus.
Treatment
Chlamydia trachomatis is treated with antibiotics. You may receive a one-time dose, or you may need to take the medication daily or multiple times a day for five to 10 days.In most cases, the infection resolves within one to two weeks. During that time, you should abstain from sex. Your sexual partner or partners also need treatment even if they have no signs or symptoms. Otherwise, the infection can be passed back and forth between sexual partners.
Having chlamydia or having been treated for it in the past provides no immunity against reinfection in the future.


1 Comments
Very useful information was shared by author. It’s really help for to know more information about Signs and symptoms of chlamydia.